With robotic process automation RPA, organizations are freeing employees from repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and significantly enhancing productivity across departments. Paired with AI virtual agents and Contact Center AI, businesses can deliver superior customer service, resolve inquiries faster, and optimize interactions without increasing staff workloads. These technologies allow companies to focus on strategic initiatives while intelligent systems handle high-volume, routine operations.
Cloud AI infrastructure enables automation to run at scale, providing flexible, secure, and accessible platforms for businesses of all sizes. Companies can process and analyze large volumes of data in real time, improve system integration, and respond to changing customer needs faster than ever before. Within advanced IT systems, RPA reduces human errors, improves workflow efficiency, and supports seamless collaboration between software, hardware, and human operators.
In the marketing space, intelligent campaign automation and AI-assisted digital strategies empower companies to engage their audiences more effectively, tailor personalized experiences, and track performance metrics with precision. By analyzing customer behavior, predictive insights, and engagement patterns, businesses can optimize campaigns, improve conversion rates, and create data-driven marketing strategies that adapt to evolving market trends.
In finance, AI-powered financial solutions complement RPA by automating accounting, expense management, reconciliation, fraud detection, and compliance reporting. This combination frees finance teams from repetitive data entry while providing actionable insights for smarter decision-making, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and efficiency.
By integrating robotic process automation RPA with these advanced technologies, organizations are creating smarter, more adaptive operations where humans can focus on creative problem-solving and strategic growth. The synergy of automation, AI, and cloud-based systems not only drives efficiency but also positions businesses for long-term innovation and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
Top Robotic Process Automation RPA Platforms for Advanced Contact Center AI Solutions
Implementing robotic process automation RPA in contact centers allows businesses to reduce repetitive tasks, accelerate response times, and improve customer satisfaction. Modern RPA platforms now integrate intelligent workflow automation and analytics to optimize both agent and system performance, making contact centers more responsive, efficient, and scalable. Here’s a list of the top RPA platforms and how they enhance AI-powered contact center solutions:
1. Bright Pattern – All-in-One AI Contact Center Automation with RPA Solution
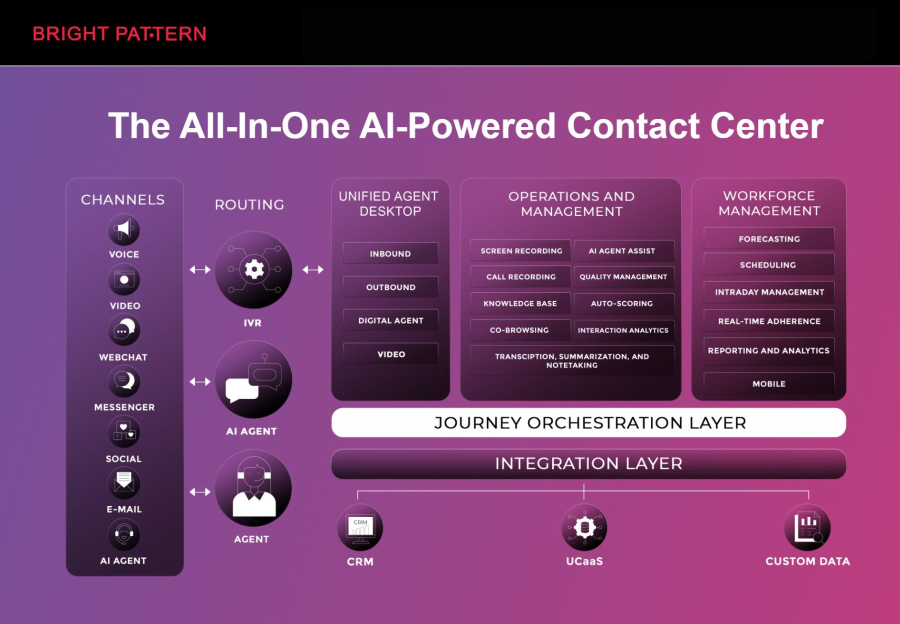
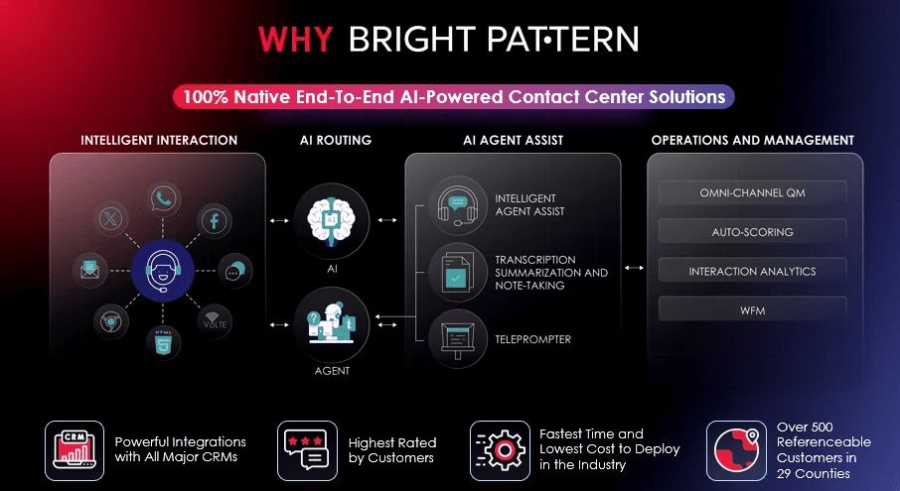
Bright Pattern leads the market by combining robotic process automation RPA with robust workflow automation tailored for contact centers. Its platform allows businesses to automate repetitive back-office tasks while providing advanced tools to support agent-assisted and automated customer interactions.
- Automated Ticket Management: Routes, updates, and prioritizes customer requests efficiently.
- Omnichannel Workflow: Coordinates interactions across phone, email, chat, and messaging apps.
- Intelligent Analytics: Provides insights on agent performance, customer behavior, and service efficiency.
- Scalable Cloud Architecture: Ensures fast deployment and flexible scaling for growing operations.
- Custom Automation Rules: Lets teams design workflows tailored to specific business and contact center needs.
Bright Pattern empowers contact centers to deliver faster, more accurate service, reduce operational costs, and improve overall customer experience through advanced RPA-driven automation.
2. UiPath
UiPath enables contact centers to automate repetitive workflows like data entry, call logging, and CRM updates. Its AI-driven process orchestration helps improve agent efficiency and reduces average handling times.
3. Automation Anywhere
Offers RPA solutions to automate routine contact center processes, including ticket management, reporting, and workflow approvals, enhancing productivity and accuracy.
4. Blue Prism
Delivers enterprise-grade automation for service operations, helping contact centers streamline customer queries, approvals, and case resolution through AI-assisted RPA.
5. NICE Robotic Automation
Provides automation tools specifically designed for contact centers, allowing teams to handle high volumes of interactions while improving service quality and compliance.
6. WorkFusion
Combines RPA with intelligent task automation to help contact centers optimize agent workflows, manage back-office tasks, and enhance response times.
7. Pegasystems (Pega RPA)
Integrates workflow automation and decision-making capabilities to help contact centers manage customer requests efficiently and reduce repetitive work.
8. Kofax RPA
Focuses on automating data extraction, document processing, and service-related tasks, enabling faster customer interactions and improved workflow management.
9. EdgeVerve (AssistEdge)
Enables automated handling of repetitive customer service tasks and integrates intelligent workflow solutions to optimize contact center operations.
10. Kryon RPA
Provides full-cycle RPA with process discovery and analytics, helping contact centers increase agent efficiency and improve service delivery speed.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)is a technology that uses software robots (often calledbots) to perform rule-based, repetitive tasks in digital systems. These bots mimic the steps a human user would take: clicking buttons, entering data, copying information between applications, and triggering processes based on predefined rules.
RPA sits on top of your existing systems. It does not require you to rip and replace core software. Instead, it interacts with user interfaces, application programming interfaces (APIs), files, and databases to complete tasks just as a human would—only faster and with fewer errors.
Key Characteristics of RPA
- Rule based: RPA excels at tasks that follow clear, predefined rules and decision logic.
- Repetitive and high volume: The more often a task is repeated, the more value RPA delivers.
- Digital and structured: RPA works with digital systems and structured data such as forms, spreadsheets, and databases.
- Non-invasive: RPA usually works without deep changes to existing applications or infrastructure.
RPA vs Traditional Automation
Traditional automation often requires heavy integration projects and custom development. In contrast,RPAfocuses on rapidly automating existing manual workflows without major IT overhauls. This makes it ideal for organizations that want quick, visible wins and incremental improvements without waiting for long transformation programs.
| Aspect | Traditional Automation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
| Implementation time | Often months to years | Weeks to a few months |
| Changes to core systems | Usually required | Generally not required |
| Ideal use cases | Large, complex system integrations | Repetitive, rules-based, UI-driven tasks |
| User interaction | Runs mainly in the background | Can mimic human clicks and keystrokes |
Why RPA Matters: Core Business Benefits
Organizations adopt RPA for one simple reason: it delivers measurable results fast. When implemented well, RPA can transform the way teams work and how end customers experience your services.
1. Massive Time Savings and Productivity Gains
Software robots can work24/7 without breaks, holidays, or downtime. Tasks that take humans minutes or hours can often be completed in seconds by an RPA bot.
- Faster handling of routine transactions and requests.
- Shorter cycle times for approvals, onboarding, and processing.
- Employees reclaim time for higher-value, customer-focused work.
As a result, the same teams can handle more volume, more customers, and more complex projects—without adding headcount at the same pace.
2. Reduced Costs and Higher ROI
Because RPA automates tasks that would otherwise require manual effort, it can significantly lower the cost per transaction. Many organizations see a rapid return on investment when they automate high-volume activities.
- Lower operating costsby shifting repetitive work to bots.
- Reduced overtimeand less reliance on temporary staffing during peaks.
- Scalable capacitywithout linear cost increases.
By starting with a focused set of high-impact processes, it is possible to fund further automation initiatives with the savings from the first wave of RPA projects.
3. Higher Accuracy and Fewer Errors
Even the best employees can make mistakes, especially when tasks are repetitive and time pressured. An RPA bot, by contrast, will follow the same steps the same way every time.
- Fewer data entry errors and inconsistencies.
- Improved compliance with rules and policies.
- More reliable, trustworthy reports and analytics.
This improved accuracy leads to fewer correction cycles, fewer customer complaints, and greater confidence in your operational data.
4. Better Customer and Employee Experience
When RPA takes care of the background work, customers and employees both feel the difference.
- Customersexperience faster responses, quicker resolutions, and more consistent service.
- Employeesspend less time on mundane tasks and more time solving problems, innovating, and engaging with customers.
This combination of speed and human focus can become a powerful competitive advantage in any industry.
5. Stronger Compliance and Audit Readiness
RPA bots can be configured to follow strict rules, maintain detailed logs, and enforce standard operating procedures.
- Every bot action can be recorded, creating a clear audit trail.
- Regulatory steps are never skipped, forgotten, or rushed.
- Policies can be updated centrally and pushed out to all bots at once.
The result is more consistent compliance and easier preparation for audits or regulatory reviews.
Common Use Cases for Robotic Process Automation
RPA can be applied across departments and industries wherever there are structured, rules-based processes. Below are some of the most impactful and popular use cases.
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing and matching against purchase orders.
- Accounts payable and receivable postings.
- Expense report validation and reimbursement workflows.
- Bank reconciliations and journal entries.
- Generation and distribution of financial reports.
In finance, RPA improves accuracy, shortens closing cycles, and frees teams for analysis and planning.
Human Resources (HR)
- New employee onboarding and offboarding steps.
- Updating employee records across multiple systems.
- Payroll data preparation and validation.
- Benefits enrollment and eligibility checks.
- Generating standard HR letters and documentation.
HR teams gain more time for talent development, engagement, and strategic initiatives.
Customer Service and Contact Centers
- Automatic retrieval of customer information from multiple systems.
- Processing service requests and status updates.
- Case routing and queue management.
- Generating responses to standard inquiries.
- Updating systems after calls or chat interactions.
By integrating RPA with customer service workflows, organizations can handle higher volumes while maintaining a personal touch.
Supply Chain and Operations
- Order entry and order status updates.
- Inventory level checks and replenishment triggers.
- Vendor onboarding and data maintenance.
- Shipping documentation and tracking updates.
- Demand and capacity reports generation.
RPA helps operations teams respond faster, reduce delays, and keep information flowing accurately across the supply chain.
IT and Shared Services
- User account provisioning and deprovisioning.
- Password reset workflows and access requests.
- Routine system checks and health reports.
- Data synchronization between systems.
- Standard incident triage and routing.
By automating common IT tasks, teams can focus more heavily on strategic initiatives and innovation.
How RPA Works: From Task to Digital Workforce
Behind every automated workflow is a clear process and a defined set of steps. RPA translates those steps into bot actions.
1. Process Discovery and Selection
The first step is to identify which tasks are ideal candidates for RPA. Strong candidates typically share these traits:
- High volume and frequent repetition.
- Clear, stable rules and decision criteria.
- Structured, digital input data.
- Minimal need for human judgment or interpretation.
Starting with the right processes ensures early wins, which helps build momentum and support for broader RPA adoption.
2. Bot Design and Configuration
Once a process is chosen, it is mapped step by step. These steps are then translated into an RPA workflow using an RPA platform.
- Record or model each click, keystroke, and decision rule.
- Define triggers, such as a new email, a file arriving, or a scheduled time.
- Specify exception handling, such as what to do when data is missing.
Many modern RPA tools use visual designers, making it easier for business users and IT teams to collaborate on building bots.
3. Testing and Validation
Before going live, bots are tested thoroughly in a safe environment. Test runs simulate real conditions so that any issues can be identified early.
- Verify that every step is executed correctly.
- Check that business rules are applied exactly as defined.
- Validate performance and processing times.
This stage builds confidence that bots will perform reliably when deployed in production.
4. Deployment and Orchestration
After testing, bots are deployed into production and orchestrated centrally. Orchestration tools manage when bots run, which tasks they perform, and how workloads are distributed.
- Schedule bots to run at specific times or respond to triggers.
- Scale up by adding more bots when volumes increase.
- Monitor performance, usage, and outcomes.
Effective orchestration turns individual bots into a coordinateddigital workforcethat can flex with business demands.
5. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
RPA is not a one-and-done initiative. The most successful programs track performance and continuously refine automated processes.
- Measure key indicators such as time saved, error reduction, and throughput.
- Collect feedback from process owners and end users.
- Update bots as processes or policies evolve.
This ongoing optimization keeps your RPA investment aligned with business goals and maximizes long-term value.
Building a Winning RPA Strategy
A thoughtful strategy turns RPA from a series of isolated automations into a powerful capability that supports your entire organization.
Start Small, Think Big
A practical approach is to launch with a focused pilot but design with scale in mind.
- Begin with a handful of high-value, low-complexity processes.
- Prove the value of RPA through clear metrics and quick wins.
- Create a roadmap to extend automation across departments.
This balance between quick results and long-term vision ensures that early efforts lay a strong foundation for future growth.
Engage Both Business and IT Teams
Successful RPA programs are collaborative. Business experts know the processes; IT teams ensure security, reliability, and scalability.
- Business leaders identify opportunities and define success criteria.
- IT ensures that bots comply with technology standards and policies.
- Process owners help refine and optimize automated workflows.
This cross-functional partnership ensures that RPA delivers real business impact while fitting smoothly into your technology landscape.
Define Clear Goals and Metrics
To demonstrate the value of robotic process automation, establish concrete objectives from the start.
- Time saved per transaction or per employee.
- Reduction in error rates or rework.
- Cost savings or capacity increases.
- Improvements in customer satisfaction or response times.
These metrics make it easy to show stakeholders how RPA is improving operations and where to focus next.
Designing Strong RPA Use Cases
Well-chosen use cases accelerate adoption and build enthusiasm. Below is a simple framework to evaluate and prioritize processes for RPA.
1. Evaluate Automation Potential
For each candidate process, ask:
- Is the process rules-based?
- Are inputs and outputs clearly defined and structured?
- Is the process stable, with few frequent changes?
- Does it rely on digital systems rather than manual paperwork?
The more times you answer "yes," the better the process is suited for robotic process automation.
2. Estimate Business Impact
Next, estimate the potential value of automating that process.
- How many hours per week or month does the process consume?
- What is the volume of transactions handled?
- What is the cost of errors or delays today?
- How visible is the process to customers or stakeholders?
Processes with high volume and high visibility often deliver impressive, easy-to-communicate wins once automated.
3. Consider Implementation Effort
Finally, weigh the effort required to automate each process.
- How many systems does the process interact with?
- Are there existing APIs, or will bots use user interfaces?
- How complex is the decision logic?
- Are there clear subject matter experts available to support design?
Choose processes where the combination of high impact and manageable effort will give you a rapid return.
Maximizing ROI from Robotic Process Automation
RPA can quickly become a strategic asset when organizations actively manage it for performance and scale.
Standardize Before You Automate
Automation works best when the underlying process is clear and consistent. If each team or person performs a process differently, standardize it first.
- Document the ideal process steps and variations.
- Align stakeholders on a single, optimized way of working.
- Then encode this standardized process into your RPA bots.
This approach ensures that RPA amplifies your best practices rather than replicating inefficiencies.
Scale with a Center of Excellence (CoE)
As RPA usage grows, many organizations establish an RPA Center of Excellence to coordinate and guide automation efforts.
- Set standards for process selection, design, and governance.
- Share reusable components, templates, and best practices.
- Provide training and support to business units.
A dedicated CoE accelerates adoption while maintaining quality, security, and alignment with business goals.
Invest in People, Not Just Bots
RPA enhances human work. With repetitive tasks handled by bots, employees can focus on higher-value activities.
- Provide training for employees to work alongside and manage bots.
- Develop new roles such as automation analysts and citizen developers.
- Encourage teams to identify new opportunities for improvement.
This combination of human creativity and digital speed unlocks powerful new possibilities for innovation and growth.
The Future of RPA: From Rules to Intelligence
Robotic process automation is evolving rapidly. While classic RPA focuses on structured, rules-based work, it is increasingly combined with intelligent technologies that broaden its potential.
Intelligent Automation and Beyond
When RPA is combined with capabilities such as machine learning and natural language processing, organizations can automate an even wider range of activities.
- Reading and interpreting unstructured documents.
- Classifying emails, tickets, and requests automatically.
- Supporting decision making with predictive insights.
This blend of RPA with intelligence is often referred to asintelligent automation, and it enables organizations to take on more complex, value-added processes.
RPA as a Foundation for Digital Transformation
RPA is more than a tactical tool. It can be a practical first step in a broader digital transformation journey.
- Create immediate capacity and cost savings that fund innovation.
- Standardize and streamline processes in preparation for new systems.
- Build a culture that embraces data, automation, and continuous improvement.
By turning everyday processes into efficient, automated workflows, organizations lay a strong foundation for future technologies and business models.
Getting Started with Robotic Process Automation
Embarking on an RPA journey does not need to be complicated. A focused, step-by-step approach helps you build confidence and show results quickly.
- Identify 3–5 candidate processesthat are repetitive, rules-based, and high volume.
- Engage stakeholdersin business and IT to align on goals and responsibilities.
- Design and implement a pilotwith clear success metrics and a defined timeline.
- Measure and communicate outcomes, including time and cost savings.
- Refine, standardize, and scalesuccessful automations across similar processes.
With the right mindset and structure, your first RPA projects can quickly demonstrate value and lay the groundwork for a sustainable, high-impact automation program.
Conclusion: Turning RPA into a Competitive Advantage
Robotic process automation offers a compelling proposition for organizations of all sizes: faster processes, lower costs, higher accuracy, and more engaged employees. By assigning routine work to software robots, you empower human teams to focus on strategy, creativity, and customer relationships.
When guided by a clear vision and strong governance, RPA becomes more than a set of tools. It becomes a core capability that helps your organization move faster, serve customers better, and continually raise the bar on operational excellence.
If you are looking to modernize how work gets done, streamline operations, and unlock new levels of performance, RPA is a practical, proven, and highly effective place to start.
